Here is an insight of WAEC Economics Objective Questions 2020
PAPER 1 [Objective]
Answer ALL questions in this section.
Shade your answers on the answer booklet provided.
1. Scarcity in economics means that _______
A. human wants are limitless
B. the economy has very few resources
C. the economy can scarcely produce anything
D. resources are limited.
2. Air is essential to life but commands no price! But Diamond is not essential to life but commands a high price! This is the paradox of ______
A. thrift B. value C. abundance D. scarcity.
3. Economics of scale operate only when ______
A. marginal cost is falling with input
B. average cost is falling with input
C. fixed cost is variable
D. variable cost is less than the fixed cost.
4. Efficiency in production involves _______
A. reducing the size of the workforce
B. producing a given output with the lowest cost combination of factors of production
D. increasing the quantity of the fixed factor of production.
5. An effect of inflation is that it ___________
A. discourages trade by barter
B. favours debtors at the expense of creditors
C. increases the real income of salary earners
D. increases the value of a country’s exports.
6. What could be the opportunity cost of a nuclear power station?
A. the running costs of the power station
B. a coal-fired power station
C. the current value of the power station
D. the cost of building the power station.
7. The diagram below shows a production possibility curve for maize and cotton.
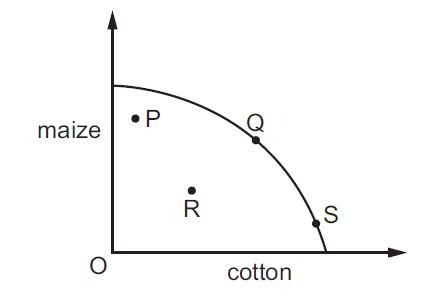
Bad weather causes a poor harvest for both crops. Which movement could be used to represent this change?
A. P to R B. Q to R C. S to Q D. S to R.
8. The market for a good was in equilibrium. A change occurred which resulted in a new equilibrium with a higher price for the good and a lower quantity traded.
What change would have caused this?
A. the demand curve moved to the left
B. the demand curve moved to the right
C. the supply curve moved to the left
D. the supply curve moved to the right.
9. A demand curve shows the relationship between the quantity demanded and ________
A. a change in income
B. consumer tastes
C. the supply of the product
D. the price of the product.
10. A government subsidises the production of pineapples. This is likely to _______
A. increase the price of pineapples
B. raise the costs of supplying pineapples
C. raise revenue for the government
D. cause the supply of pineapples to increase at every price.
11. What indicates the existence of external costs in an economy?
A. An international trade deficit has caused the country to be in debt.
B. National companies have borrowed from foreign investors.
C. Private costs of production are less than social costs.
D. Private costs of production are more than social benefits.
12. What might be a disadvantage to a trade union when arguing for an increase in its members’ pay?
A. an increase in imports of a cheaper, similar product
B. the closure of a local training college resulting in fewer potential workers
C. the development of a new and profitable brand of the company’s product
D. the development of new techniques that increase productivity.
13. A German car manufacturer decided to produce its cars in a factory in China. What would not be a reason why they might have chosen to do this?
A. cheaper wage costs in China
B. the availability of raw materials
C. to gain external economies from skilled labour in China
D. to increase Germany self-sufficiency.
14. A government removed the quota on goods imported into the country.
What is the most likely result of this?
A. a decrease in demand for domestic production
B. a decrease in domestic unemployment
C. a decrease in exports
D. a decrease in the balance of trade deficit.
15. A modern corporation is owned by ________
A. debenture holders B. ordinary shareholders C. preference shareholders D. creditors.
16. One of the most important factors that should be considered in the location of an industry is _________
A. nearness to the financial centre
B. assured patronage by government functionaries
C. availability of inputs and market
D. availability of adequate security.
17. What is the term used to describe a policy aimed at promoting the local production of goods which are usually imported?
A. deregulation B. import substitution C. tariff reduction D. backward integration.
18. Progressive tax structure is designed to ___________
A. take more from the income of the poor
B. take more from the income of the rich
C. take equal proportion of income from both the rich and the poor
D. reduce the problems emanating from tax imposition.
19. Which of the following best describes the production function?
A. it indicates the best output to produce
B. it relates naira inputs to naira outputs
C. it relates physical outputs to physical inputs
D. it indicates the best way to combine factors to produce any given output.
20. Which of the following reward is associated with entrepreneurship as a factor of production?
A. salaries B. profits C. interest D. rents.
21. In a market economy, the question of what, how and for whom to produce are solved by the ________
A. elected representative of the people
B. planning committee
C. price mechanism
D. government.
22. At any given level of output, a firm’s total variable cost equals ________
A. total cost less marginal cost
B. total cost less total fixed cost
C. total cost less average cost
D. average variable cost and marginal variable cost.
Age groups (years) Distribution (%)
Above 60 30
15 – 60 45
0 – 14 25
23. From the above, the estimated dependency ratio of the population shown above is _______ A. 11: 9 B.9: 11 C. 7: 3 D. 3: 7
23. Which of the following factors is NOT responsible for the rural /urban drift in Nigeria?
A. the infrastructural facilities in the cities
B. declining fertility of rural farmlands
C. rural electrification programme
D. higher living standards in urban areas.
24. The necessity of choice is due to the fact that _______
A. human wants are inelastic
B. customers like to maximize satisfaction
C. resources are abundant
D. consumers are selective.
25. What is meant by labour supply?
A. number of people in working population
B. number of men and hours they work
C. number of hours during which the middle-aged persons work
D. number of workforce multiplied by the hours they worked.
26. Any payment to a factor of production in excess of what is necessary to keep its present employment is known as ________
A. real income B. profit C. economic rent D. real wage
27. The market where there are many differentiated products is called ______
A. monopoly B. perfect competition C. monopolistic competition D. Oligopoly.
