Biology Practical Neco Answers 2024
1ai)
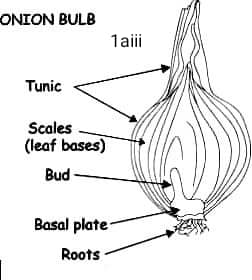
Spec: A – Onion (Bulb)
Spec: B-Ginger (Rhizome)
Spec: C – Irish Potato (tuber)
Spec: D – Potted Bean seedling (A week old)
Spec: E – Potted Guinea-com seedling (A week old)
(1aii)
Spec A: Vegetative propagation (by bulbs)
Spec B: Vegetative propagation (by rhizomes)
Spec C: Vegetative propagation (by tubers)
(1aiii)

(1aiv)
Specimen D: Epigeal germination (the seedling emerges from the soil and the cotyledons are above ground)
Specimen E: Hypogeal germination (the seedling remains underground and the cotyledons remain below ground)
(1av)
Specimen D;
(i)The seedling needs light to grow and develop
(ii)The cotyledons are photosynthetic and need to be above ground to perform photosynthesis
Specimen E :
(i)The seedling gets protection from harsh environmental conditions
(ii)The cotyledons can absorb nutrients from the soil without being exposed to light
(1avi)
Specimen D: Tap root system (a single main root that grows straight down into the soil)
Specimen E: Fibrous root system (many branching roots that spread out in all directions)
(1avii)
SPECIMEN D: Reticulate venation (net-like pattern of veins in the leaf)
Specimen E: Parallel venation (veins run parallel to each other in the leaf)
(1aviii)
Specimen; A – Onion (Bulb): Scale leaves (the thick, fleshy leaves that make up the bulb)
Specimen; B – Ginger (Rhizome): Rhizome (the underground stem that serves as a storage organ)
Specimen; C – Irish Potato (Tuber): Tuber (the underground stem that serves as a storage organ, consisting of starch and other nutrients)
•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••
(2ai)
Specimen; F – Pigeon’s head with the neck
Specimen; G- Atlas vertebra of a Rabbit
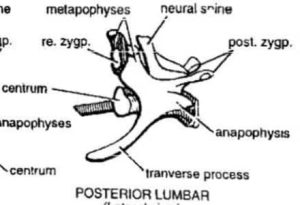
Specimen; H- Lumbar vertebra of a Rabbit
Specimen; I-Cactus plant
Specimen; J – Water lettuce
(2aii)
To support the head and allow for flexibility and movement of the neck.
(2aiii)
Specimen G:
First cervical vertebra (C1), located at the base of the skull
Specimen H:
Located in the lower back region, between the ribcage and the pelvis (L1-L7)
(2aiv)
Occipital bone
(2av) 
(2avi)
Mammalia.
(2avii)
Specimen I; Cactus plant
(i)Stem succulence (ability to store water in the stem)
(ii)Spines (reduce water loss through transpiration)
(iii)Deep roots (access water deep in the soil)
Specimen J; Water lettuce
(i)Floating leaves (allow the plant to stay afloat on the water surface)
(ii)Long stems (allow the plant to absorb nutrients from
(3ai)
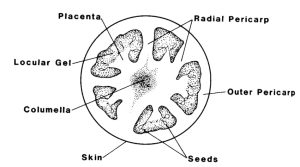
Specimen; K-Ripe Tomato fruit
Specimen; L – Ripe Palm fruit
Specimen; M-Ripe Tridax fruit
Specimen; N – Ripe Mango fruit
Specimen; O-Ripe flamboyant flower.
(3aii)
Specimen K; Berry
Specimen L; Berry
Specimen M; Cypsela
(3aiii)
Specimen K; Axile
Specimen N; Axile
(3aiv)
Specimen L; Dispersal by Animal
Specimen M; Dispersal by wind
(3av)
(i)Hooks
(ii)Lightweight
(iii)Sticky surface
(3avi)
Specimen K
(i)Small sized
(ii)Red coloured
Specimen
(i)Big sized
(ii) Yellow coloured


What of all the subject remaining